



Fire Alarm Voltage
When installing or maintaining a fire alarm system, one of the most important factors to consider is the voltage that powers the system. Fire alarms require a stable and reliable power source to ensure that they function correctly in the event of a fire. Understanding the voltage requirements is crucial for both the safety of the building occupants and the effectiveness of the alarm system.
In general, fire alarms are powered by either low voltage (DC) or high voltage (AC) depending on the type of system and the configuration. These systems must meet specific voltage standards to comply with fire safety regulations. This guide will provide an overview of the typical voltage requirements for fire alarm systems, ensuring you have the correct information for installation or troubleshooting.
Common Voltage Requirements for Fire Alarms
-
Low Voltage (DC): The majority of fire alarm systems operate on low-voltage DC circuits, typically ranging
from 12V to 24V DC. This voltage range is often used for control panels, smoke detectors, heat detectors, and other
peripheral devices in fire alarm systems.
-
12V DC Systems: Some basic or smaller fire alarm systems operate on 12V DC power. These systems are often used for
residential applications or in buildings with fewer alarms.
-
24V DC Systems: More commonly, fire alarm systems, especially those used in commercial buildings or larger facilities, use
24V DC circuits. These systems are more reliable and provide better compatibility with larger or more complex fire alarm setups.
-
12V DC Systems: Some basic or smaller fire alarm systems operate on 12V DC power. These systems are often used for
residential applications or in buildings with fewer alarms.
-
AC Voltage for Fire Alarm Control Panels: In certain instances, fire alarm control panels may be powered by AC
voltage,
often 120V or 240V AC. The control panels are then connected to low-voltage DC circuits to power the detectors, alarms, and
other components. In these systems, AC voltage is used to power the main control panel, which in turn powers the rest of the system.
Key Components and Their Voltage Requirements
-
Fire Alarm Control Panel (FACP): The heart of the fire alarm system, the FACP is usually powered by 120V
AC
or 240V AC, but its output is typically 12V or 24V DC to power peripheral devices like alarms, detectors,
and sirens.
-
Smoke and Heat Detectors: These devices are generally powered by 24V DC, as they are directly connected to
the control panel. Some smoke detectors may use 12V DC in simpler setups.
-
Manual Pull Stations: These devices that allow individuals to manually trigger the alarm are usually wired into the system
using low voltage DC lines, typically 12V or 24V.
-
Notification Appliances (Sirens, Strobes, and Horns): These notification devices often require 24V DC for
operation, as they need to be loud and consistent in alerting the building occupants.
-
Auxiliary Devices (Doors, Dampers, etc.): Some additional components in the fire alarm system, such as fire doors or
ventilation dampers, may be powered by 24V DC or 120V AC, depending on the design and installation
specifications.
Why Voltage Is Important for Fire Alarm Systems
-
Reliability and Compliance: Fire alarms must meet specific voltage standards to comply with safety regulations and ensure
the system’s reliability. Incorrect voltage can cause the system to malfunction, leaving occupants vulnerable in the event of a fire.
-
Compatibility: Understanding the voltage requirements helps ensure that all components of the fire alarm system are
compatible with each other. For instance, if the fire alarm panel operates on 24V DC, but the detectors are designed for 12V DC, the system
will not work as intended.
-
Battery Backup: Many fire alarm systems include a battery backup to ensure they continue functioning during a power outage.
In these cases, understanding the voltage is critical for selecting the appropriate battery type and ensuring that it meets the system’s
requirements.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the voltage of a fire alarm system plays a crucial role in its operation and performance. Most fire alarm systems operate on 12V or 24V DC, especially for detectors, sirens, and control panels. Some systems may also incorporate 120V or 240V AC for powering the main control panels, which then distribute the appropriate low voltage to the rest of the system.
When installing or servicing a fire alarm system, it’s essential to ensure that all components are properly powered to guarantee the system works effectively and complies with fire safety regulations. Always consult with a professional technician or follow manufacturer guidelines to ensure the correct voltage is used for your specific fire alarm system.
Product information:
Style: Handheld Multimeter
Use: professional use
Specifications: ZL126A (battery type),ZL126B (rechargeable),ZL128A (battery type),ZL128B (rechargeable)
Size: 162*48*27MM
Charging method: USB
Packing list:
Multimeter * 1
Cloth bag * 1
Packaging box * 1
Instructions * 1
Temperature test line * 1
Charging cable * 1
Pen * 1
Product Image:
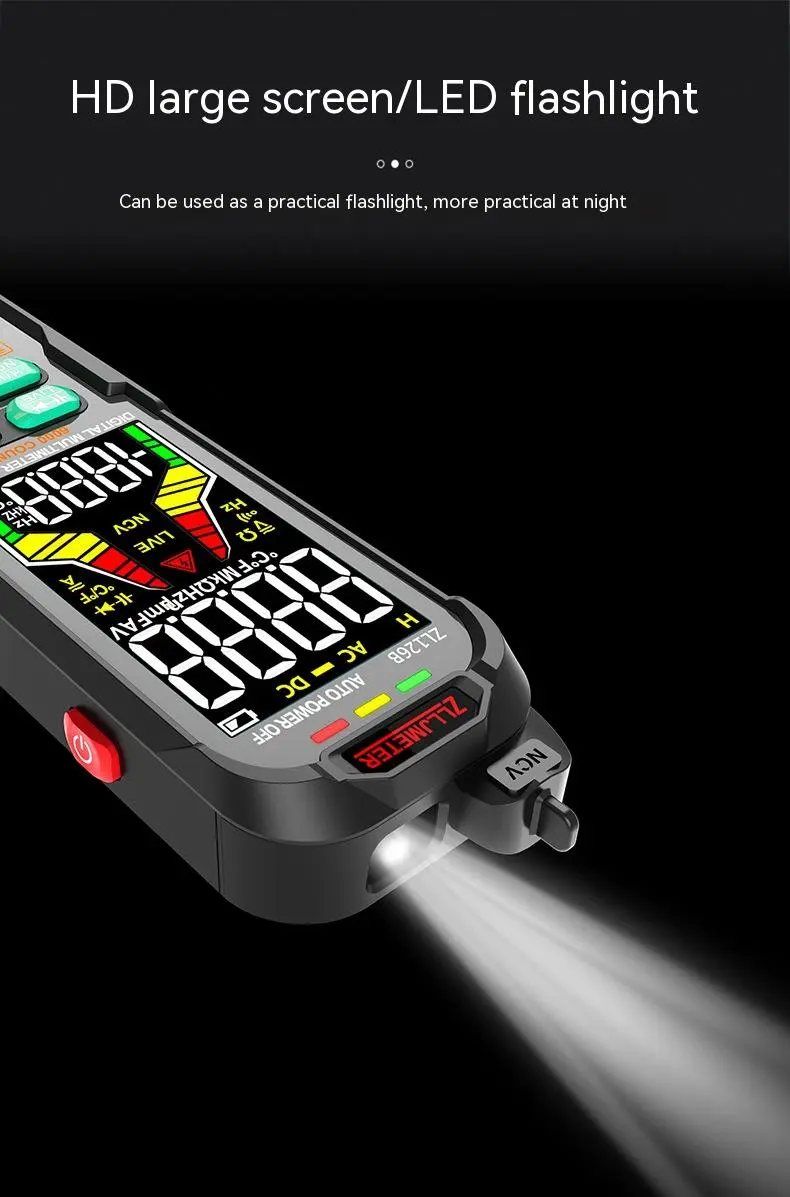








The product may be provided by a different brand of comparable quality.
The actual product may vary slightly from the image shown.
Shop amazing plants at The Node – a top destination for plant lovers








.png)






.jpg)









.jpg)





.jpeg)





.jpeg)



.jpeg)








.jpeg)



.jpeg)

.jpeg)

.jpeg)

.jpeg)




.jpeg)
.jpg)

.jpeg)






.jpeg)
.jpeg)




.jpeg)





.jpeg)


.jpeg)

.jpeg)

.jpeg)

.jpeg)







.jpeg)
.jpeg)
.jpeg)





.jpeg)



.jpeg)






.jpg)
.jpeg)









.jpg)


ulva-Logo.jpg)




.jpeg)



.png)















.png)























